-
Home
-
Patient Transfer Techniques for Safe, Effective Transfers
Patient Transfer Techniques for Safe, Effective Transfers
August 1, 2023
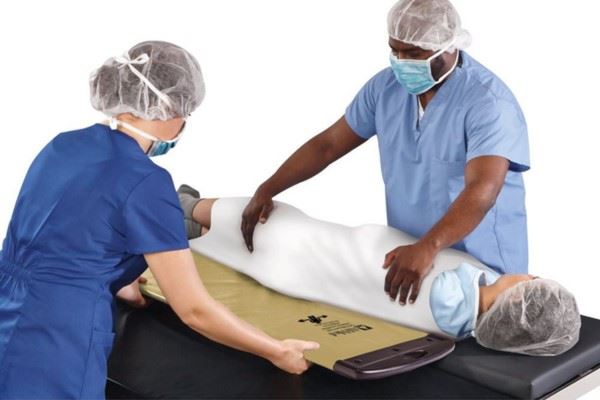
Patient transfer techniques are essential skills for many healthcare professionals. Transferring patients safely and effectively from one surface to another involves maintaining proper patient positioning, balance, and coordination throughout the process. In this article, we’ll explore the various techniques and tools used when transferring patients.
Safe Patient Transfer Techniques
Safe patient transfer techniques involve several steps, including assessing the patient's ability to participate in a transfer, preparing the environment for the transfer, and using the correct assistive devices. Before transferring a patient, caregivers should assess the patient's ability to bear weight, stability, and level of consciousness. The environment should be well-lit and free of obstacles.
Types of Transfers
There are several types of patient transfer techniques, each tailored to accommodate the individual physical ability and specific needs of the patient. Healthcare professionals should consider factors such as mobility limitations, motor skills, and medical conditions to determine the most suitable transfer method for each individual patient.
By selecting the appropriate technique, caregivers can minimize the risk of injury to both themselves and the patient while promoting patient comfort and safety. These techniques include pivot, mechanical lift, and board transfers.
- Pivot transfer: The patient moves from one surface to another with the aid of a pivot point, which is generally the patient’s feet or buttocks. It is commonly used for wheelchair transfers and is particularly beneficial for individuals with limited mobility. This transfer helps rotate the patient from one direction to the other. Patient safety belts are often used in conjunction with pivot transfers.
- Lift transfer: This technique involves the use of a mechanical or electrical device designed to safely and efficiently lift and move the patient without the need for physical lifting. This is especially helpful for patients with no mobility, and can greatly reduce both the risk of injury and number of caregivers needed during the transfer. A sling is placed snugly around the patient and attached securely to the lift to prepare for a safe transfer.
- Board transfer: Different types of boards can be used to transfer patients either laterally for those with no mobility or in a seated position for those with limited mobility. To facilitate the process, the caregiver carefully places a board beneath the patient and provides assistance as the patient moves or is moved from one surface to another.
- Air-assisted lateral transfer: Air-assisted lateral transfer systems work simillarly to air hockey tables, reducing friction by circulating low-pressure, high-volume air through hundreds of micro-perforations. This creates a cushion of air to help smoothly, comfortably, and safely lift and glide patients from surface to surface, drastically reducing overall pull force and the risk of staff injuries compared to traditional transfer devices.
Transfer Equipment
Transfer equipment is used to facilitate safe and easy transfers for both patients and caregivers. Some of the most commonly used types of transfer equipment include grab bars, gait belts, transfer sheets, shifters, rollboards, lifts and slings, transfer boards, pivot discs, and air-assisted lateral transfer systems.
- Grab Bars: Grab bars offer support for patients, enabling them to confidently and independently pull themselves up to a standing position or maintain their balance during transfers.
- Gait Belts: Also called transfer belts or patient safety belts, gait belts are commonly used in healthcare settings to provide additional support and stability to patients who may be unsteady on their feet or have weakened leg muscles. By securely fastening the transfer belt around the patient’s waist, healthcare providers can ensure a higher level of safety and confidence during transfers, thus reducing the risk of falls or injuries.
- Transfer Sheets: Slide sheets allow you to move a patient without lifting them. They come in various sizes and materials, ensuring flexibility and adaptability for different patients' needs.
- Shifters: Shifters are placed between two surfaces to safely bridge any gaps or height differences. Most models are made using materials that allow the patient to slide easily across the board for a smooth, easy transfer.
- Rollboards: The cover of a rollboard rotates around the frame and moves with the patient, acting like a conveyer belt. This gently pushes the patient from one surface to another, helping reduce the overall friction and force required.
- Lifts and Slings: Mechanical or electric lifts eliminate the need for manual lifting, helping reduce the risk of injury for staff. The patient is placed securely into a sling, which is attached to the lift to facilitate a comfortable, safe transfer.
- Transfer Boards: Transfer boards can be used with patients who have limited upper and/or lower body strength and are able to sit up while maintaining balance. These boards help facilitate transfers between two seated surfaces, such as a bed, chair, wheelchair, or toilet.
- Pivot Discs: Pivot discs are designed for use during pivot transfers with patients who can stand but cannot readily move their legs. Patient Safety belts or slings are recommended for use with pivot discs to provide additional support.
- Air-Assisted Lateral Transfer Systems: These systems help transfer patients up to 1,200 lbs. from surface to surface with only two caregivers needed. This method reduces overall pull force and decreases the risk of staff injuries. The PPS Glide Air-Assisted Lateral Transfer System also comes in Reusable or Single-Patient Use models to fit your facility’s protocol.
Effective patient transfer techniques are of utmost importance in promoting the safety and well-being of both patients and caregivers. This involves carefully assessing the patient's mobility, preparing the environment for the transfer, and utilizing the appropriate transfer equipment for added support and security.
Want more information? Visit AliMed’s Safe Patient Handling Resource Hub to explore a multitude of educational resources, including a new guidebook, printable staff training posters, podcasts, infographics, videos, and more.